Case Studies
Explore AdveData’s success stories through detailed case studies showcasing how our data analytics solutions transformed businesses across Africa. Real results, measurable impact.

A study on the classification of households in Rwanda based on factor scores
Many researchers have focused on grouping or classifying households into different categories based on either income/consumption or household assets. However, these practices may lead to an inadequate classification due to Rwanda’s unique family structure. In Rwanda, households are classified into six socio-economic classes known as `Ubudehe categories’. This classification is based on subjective perceptions of people. In this study, we propose to use household assets as well as income/consumption to classify Rwandan households into different socio-economic categories. These approaches are summated Likert scale method and factor score method. When these two methods are compared by a discriminant analysis, the factor score method brings out more reliable results than Likert method.
Bayesian Pathway selection
We propose a Bayesian pathway selection method that allows the selection of pathways (sets of genes) directly related to a continuous response variable under a non-parametric hierarchical model framework. The fact that sets of genes effectively explain more the response variable than individual genes was the driving force behind this research. We utilize the stochastic search variable selection and kernel machine method to select effective pathways after adjusting clinical covariates effects. The selection of pathways simultaneously works compared to other methods, where pathways are analyzed separately. We show that the proposed model can successfully detect effective pathways associated with outcomes through simulation studies and real data application.

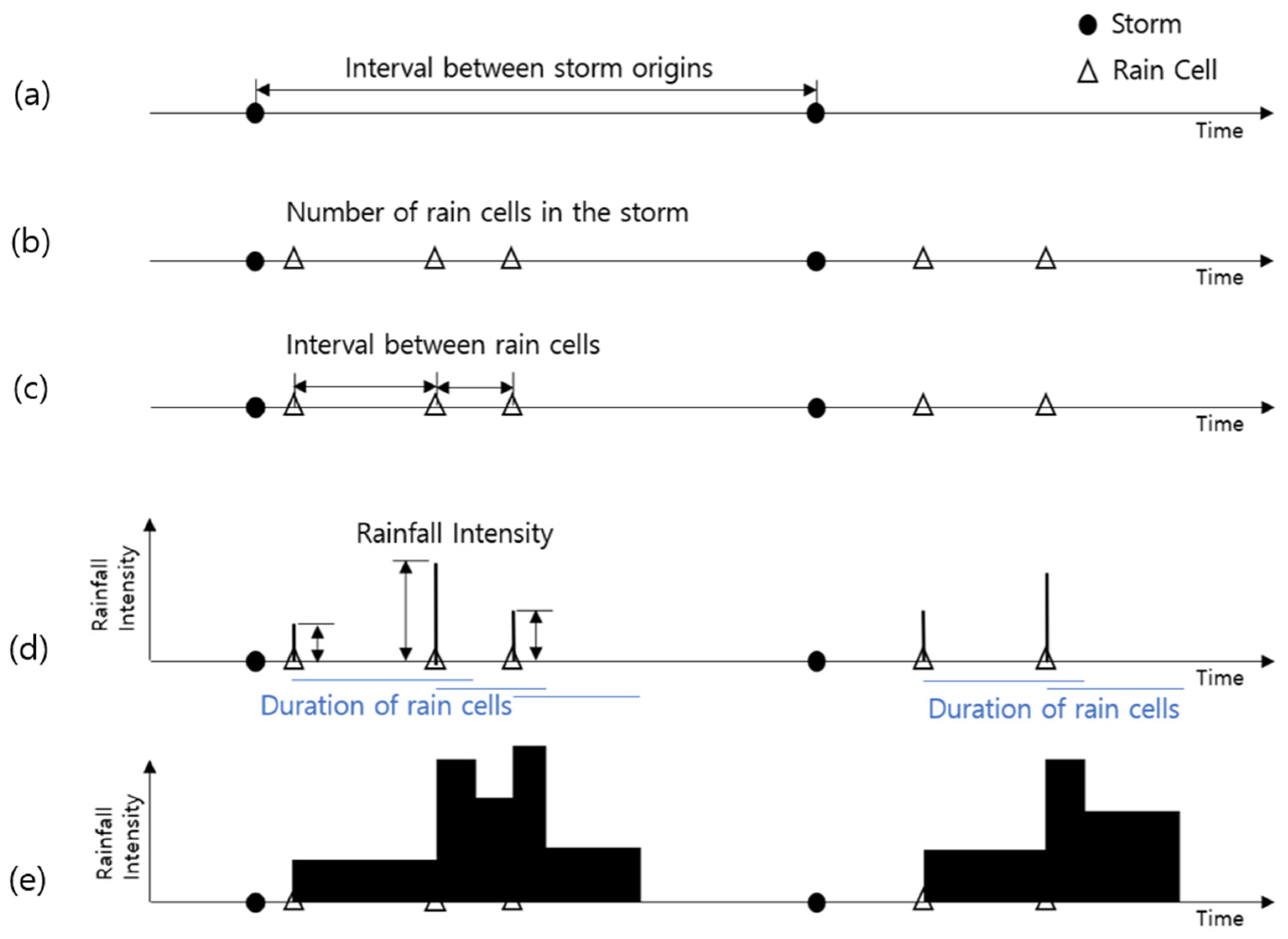
Bayesian Estimation of Neyman–Scott Rectangular Pulse Model Parameters in Comparison with Other Parameter Estimation Methods
Neyman–Scott rectangular pulse is a stochastic rainfall model with five parameters. The impacts of initial values and optimization methods on the parameter estimation of the Neyman–Scott rectangular pulse model were investigated using both the method of moments and the method of maximum likelihood. The estimates using the method of moments were influenced by the optimization method and were sensitive to the initial values and the aggregation scale of the data. Thus, by using frequentist estimation methods, we cannot guarantee the unique values as estimates. The aim of this study is to find more reliable unique values as estimates using a Bayesian approach. In this approach, parameters are estimated from the posterior distribution, and model performance is assessed by comparing observed values with fitted values. Slice sampling within the Gibbs sampler algorithm demonstrates superior convergence and model fitting, yielding unique estimates for the model parameters. The main conclusion of this study is that Bayesian estimation methods outperform other estimation methods in terms of providing reliable and stable estimates that improve rainfall generation accuracy.